[Created with Google ImageFX]
In recent years, Africa has been on the cusp of a digital revolution, particularly in mobile money. Sub-Saharan Africa remains the world leader in its adoption. Increasing urbanisation, improved internet and smartphone penetration, and a young and upwardly mobile population have encouraged the emergence of new payment options like contactless payment, as well as a more diverse consumer market.
The Future of Commerce report looks into key sectors such as e-commerce, digital payments, logistics, supply chain, and retail, analysing current trends and future trajectories.
Overview of Digital Commerce in Africa
The digital economy in Africa has become a dynamic hub of innovation over the past decade. According to GSMA, digital wallets and mobile money services will process over $500 billion in transactions across Africa by 2025. With over half a billion people on the continent becoming e-commerce users, this could potentially add up to $180bn in GDP, per the UNCTAD.
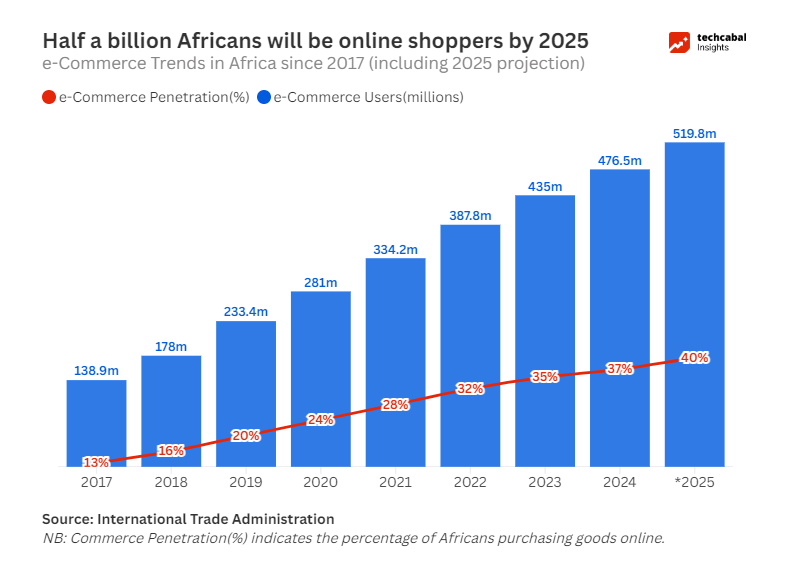
Chart: Oluwaseun Joseph/ TC Insights
Key drivers of this transformation include widespread mobile internet adoption, increased smartphone penetration, and the rise of digital payment systems. Around 61% of African connections will be on smartphones by 2025, with 33% on 4G.
Nigeria’s E-commerce Growth
Nigeria’s e-commerce market is projected to grow from $8.53 billion in 2024 to $14.92 billion by 2029, reflecting a CAGR of 11.82%. The initial growth phase was driven by B2C companies like Jumia and Konga. This was followed by a brief dominance of B2B e-commerce from 2021 to 2023. However, macroeconomic factors such as currency devaluation and reduced consumer purchasing power have impacted growth.
Despite challenges in the B2B sector, food delivery startups like Glovo and Chowdeck have thrived, leveraging changing consumer behaviours post-COVID-19. The success of these startups reflects why adapting business models to meet evolving market conditions is key to survival and growth.
South Africa and Egypt
South Africa’s e-commerce market is expected to grow by 8.4% annually, reaching $7.7 billion by 2024. An internet penetration rate of 68.2% is the key driver of this growth. Egypt is also experiencing rapid digital expansion. E-commerce sales will likely exceed $3 billion by 2024, supported by a strong fintech sector and an internet penetration rate of 57.3%.
Other African Markets
Emerging markets such as Kenya, Ghana, and Côte d’Ivoire also show growth potential. Kenya’s e-commerce market is estimated to reach $2.1 billion by 2024, fueled by mobile money services like M-Pesa. Meanwhile, Ghana’s e-commerce market is projected to expand to $1.2 billion by 2024, benefiting from a 52% internet penetration rate.
[For data requests or research services, reach out to TC Insights via this link]
Emerging Trends in Digital Commerce
Mobile-First Economy
Africa’s mobile-first approach is expected to drive over 60% of e-commerce transactions by 2025. With mobile phone adoption projected to reach 623 million unique subscribers by 2025, businesses must optimise their platforms for mobile accessibility.
Cross-Border E-commerce
Cross-border e-commerce is on course to grow at a CAGR of 13% from 2023 to 2028, largely due to initiatives like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). If implemented efficiently with lower tariffs to encourage trade, businesses could expand beyond their local markets.
Innovation in Payment Systems
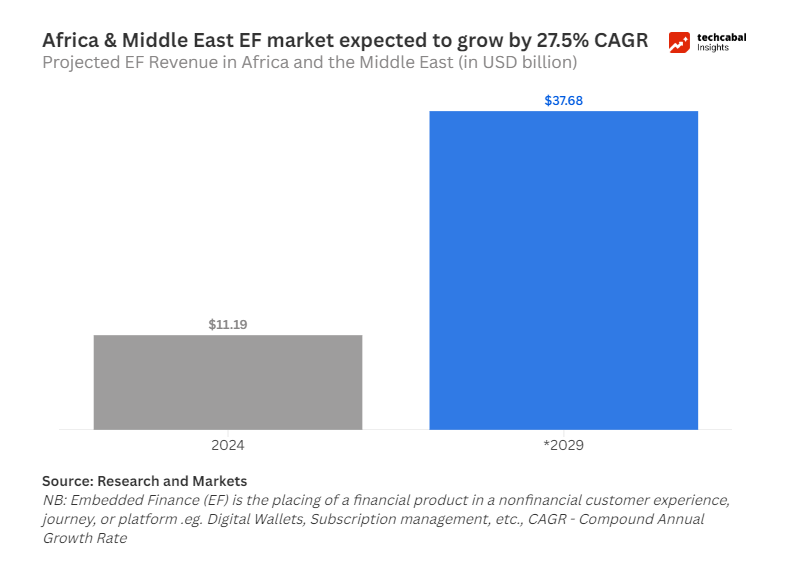
Chart: Oluwaseun Joseph/ TC Insights
The rise of embedded finance, which integrates digital banking and other financial products and services into nonfinancial applications, comes with exciting prospects. Transaction values could exceed $230 billion by 2027. Digital wallets and mobile money services will process over $500 billion in transactions by 2025, enabling broader financial inclusion.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Despite major projections pointing to growth for the African e-commerce sector, there are still significant hurdles, particularly around cybersecurity, that need to be resolved.
One report notes that Nigerian financial institutions lost over ₦1.1 trillion to cybersecurity attacks in 7 years. Africa experienced a spike in cyber-attacks. An average of 2,960 weekly incidents were reported in Q2 2024, highlighting the need for robust security measures to protect businesses and consumers.
Logistics: A Key Enabler
Last-Mile Delivery Innovations
Last-mile delivery, which focuses on the final leg of an item’s journey from the local distribution centre to the end consumer, will account for 50% of total logistics costs in African e-commerce by 2025. Innovations such as drone deliveries and automated lockers are being introduced to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Supply Chain Management Improvements
Integrating blockchain technology, AI, and IoT in supply chain management will enhance transparency, security, and operational efficiency. These innovations will help address logistical challenges and promote sustainability in the supply chain.
Conclusion
Changing consumer behaviours in line with economic fortunes means the future of African commerce is not set in stone. However, the insights provided in the report show, among other things, the importance of adaptability, innovation, and resilience for businesses operating in Africa. As Africa embraces digital transformation, stakeholders must remain agile to capitalise on emerging trends and navigate potential challenges in the coming years.
—————————————————————————————————————-
Did you enjoy this article? Learn more by clicking this link to download the full report.